- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search



Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-16 Origin: Site









Plastic pipe extrusion lines are crucial for manufacturing pipes in industries like construction and telecommunications. These systems turn raw plastic into continuous pipe products. Understanding their working principle is essential for optimizing efficiency and improving quality. In this article, we'll explore how extrusion lines work, their components, and the challenges they face.
Plastic pipe extrusion is a continuous manufacturing process in which thermoplastic materials are melted and forced through a shaping die to create hollow cylindrical pipes. These pipes are used for various applications, such as water supply, sewage systems, gas transport, and electrical conduit systems. The process allows for high-volume production with consistent quality, making it an ideal choice for industries that require large quantities of pipes in various sizes and specifications.
The materials used in plastic pipe extrusion primarily include PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), PE (Polyethylene), and PPR (Polypropylene Random Copolymer). These thermoplastics are chosen based on their properties, such as chemical resistance, durability, and flexibility. Additives like color masterbatch, stabilizers, and UV inhibitors are often mixed with the base material to enhance the performance and appearance of the final pipe product. For instance, PVC pipes are commonly used for plumbing and drainage due to their cost-effectiveness and high chemical resistance.
Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
PVC | Durable, resistant to chemicals, cost-effective | Plumbing, electrical conduit, drainage systems |
PE | Flexible, impact-resistant, and resistant to chemicals | Gas and water distribution pipes |
PPR | Heat and corrosion-resistant | Hot and cold water supply systems |
The extruder is the heart of the plastic pipe extrusion line. It consists of a barrel, a screw, and a heating system. Raw plastic pellets are fed into the barrel through a hopper. The rotating screw inside the barrel heats and melts the material while also pushing it forward. The screw design, length, and speed are optimized to ensure uniform melting and material consistency. The heated, molten plastic is then ready to be extruded through the die head.
The die head is the component that shapes the molten plastic into the desired pipe form. It features a circular opening that allows the molten plastic to exit in the shape of a pipe. The die head can be adjusted to create pipes of different diameters and wall thicknesses. Advanced die heads often include features that allow for precision control over pipe dimensions, which is critical for ensuring that pipes meet industry standards.
Once the molten plastic exits the die head, it must be rapidly cooled to solidify it into the desired shape. Cooling systems typically use water tanks or air jets to achieve this. The cooling process must be carefully controlled to avoid defects such as warping or cracking. Cooling tanks maintain the temperature of the extruded pipe, ensuring that it retains its shape and stability after solidification.
The haul-off unit is responsible for pulling the extruded pipe through the cooling system and further down the production line. This equipment maintains consistent speed and tension to ensure that the pipe does not deform. By controlling the pulling speed, the haul-off unit also helps maintain the dimensional accuracy of the pipe.
Once the pipe has been properly cooled and sized, it is cut to the desired length using cutting equipment. The cutting process is crucial for ensuring that each pipe is uniform in length and free from defects. Different cutting methods, such as rotary or planetary cutters, may be used depending on the pipe material and the requirements for precision.
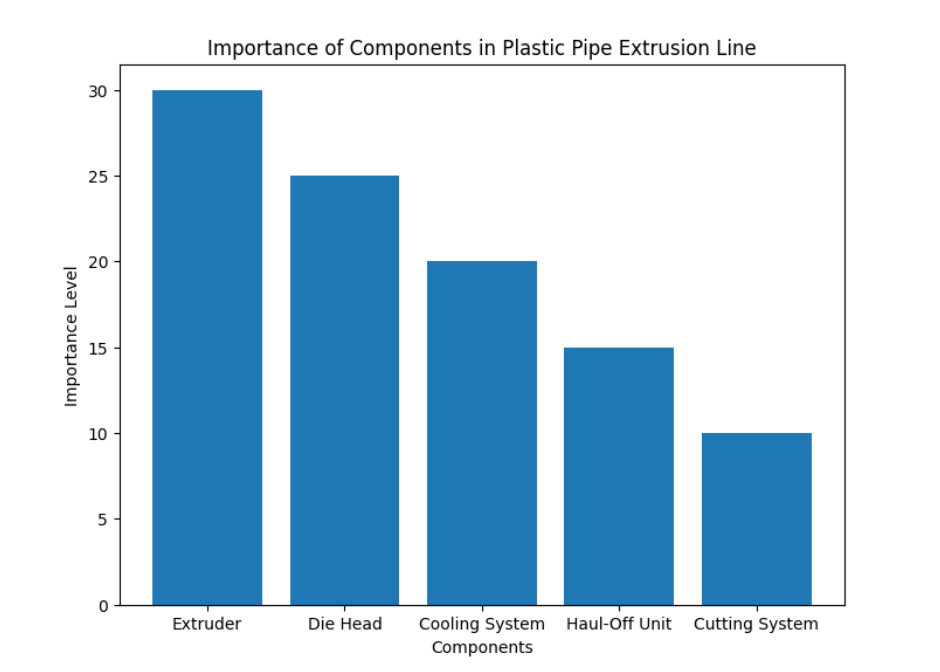
Component | Function | Importance for the Process |
Extruder | Melts and mixes plastic pellets | Central to material melting and shaping |
Die Head | Shapes the molten plastic into a pipe | Determines pipe dimensions and profiles |
Cooling System | Cools and solidifies the extruded pipe | Ensures proper solidification and prevents deformation |
Haul-Off Unit | Pulls the pipe through the extrusion line | Maintains tension and consistency in pipe size |
Cutting System | Cuts the pipe into desired lengths | Ensures precise cutting for uniform pipe lengths |
The extrusion process begins with the feeding of raw plastic pellets into the extruder. Before the pellets enter the extruder, they are often preheated to remove any moisture. Moisture in the plastic can lead to defects in the final product, such as bubbles or reduced mechanical properties. Special drying equipment ensures that the pellets are at the correct moisture level before they are introduced to the extruder.
Inside the extruder, the pellets are subjected to both heat and mechanical shear from the rotating screw. This combination of heat and pressure causes the plastic to melt and become a homogeneous melt. The screw moves the plastic material along the barrel, compressing and mixing it to ensure uniformity. The extruder’s heating zones are carefully controlled to maintain the correct temperature and pressure for the material.
Once the plastic is fully melted, it is pushed through the die head. The die head shapes the molten plastic into the desired pipe profile. The design of the die head is critical to ensuring the final pipe has the correct dimensions, smooth surface, and consistency. Adjustable die lips can fine-tune the wall thickness and diameter of the pipe.
After passing through the die, the extruded pipe is rapidly cooled to solidify the plastic. This cooling process is vital to maintaining the pipe’s integrity. Depending on the pipe size and material, the cooling system may include water tanks, air jets, or a combination of both. Proper cooling ensures that the pipe retains its shape without warping or cracking.
Sizing and calibration equipment are used to ensure that the pipe maintains the correct dimensions. This is done by applying pressure or vacuum during the cooling process to keep the pipe against the sizing sleeve. Proper calibration ensures uniform wall thickness and dimensional accuracy, which are essential for the pipe's strength and performance.
Once the pipe has been sized and cooled, it is cut to the desired length using cutting systems such as rotary or planetary cutters. In addition to cutting, marking systems can print relevant information on the pipe, such as size, production date, or material type. This ensures traceability and compliance with industry standards.
Single-layer extrusion lines are used to produce simple plastic pipes, while multi-layer extrusion lines allow for the production of pipes with multiple layers. Multi-layer pipes offer benefits such as enhanced barrier properties and improved mechanical strength. For example, multi-layer pipes with an oxygen barrier layer are used in plumbing and heating systems to improve longevity and performance.
Feature | Single-Layer Extrusion | Multi-Layer Extrusion |
Pipe Strength | Suitable for basic applications | Enhanced strength for specific uses like oxygen barrier |
Insulation | Standard insulation properties | Improved insulation and durability |
Cost Efficiency | More cost-effective | Higher cost but offers long-term benefits |
There are specialized extrusion lines designed for specific applications. For instance, gas pipes require higher pressure resistance, which calls for specific extrusion conditions. Similarly, some lines are designed for the production of high-strength industrial pipes or flexible pipes used in agriculture or drainage.
One of the challenges in plastic pipe extrusion is ensuring the compatibility of different materials. Different polymers have distinct melting points, viscosities, and processing requirements, which can complicate the extrusion process. Careful material selection and precise control of extrusion parameters are essential to avoid defects.
Maintaining the correct temperature and pressure is critical to achieving high-quality pipes. If the temperature is too high, the material may degrade; if it is too low, the plastic may not melt uniformly. Similarly, improper pressure settings can lead to inconsistent extrusion or dimensional defects in the final product.
Extrusion lines can experience downtime due to mechanical failures, material issues, or improper setup. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the system, checking for wear and tear, and calibrating the equipment, can minimize unplanned stoppages and improve overall productivity.
Modern plastic pipe extrusion lines use automation and advanced control systems to monitor and adjust various parameters in real-time. This allows for better control of the process, reduces human error, and improves efficiency. Predictive maintenance technologies can help identify potential issues before they cause downtime.
Recent innovations in plastic extrusion lines focus on improving energy efficiency. Servo motors, optimized heating systems, and advanced cooling technologies reduce energy consumption and operational costs. These innovations contribute to sustainability and lower the overall environmental impact of production.
As sustainability becomes more important in manufacturing, many extrusion lines are designed with environmental considerations in mind. This includes reducing waste, recycling materials, and using eco-friendly additives. By implementing these practices, manufacturers can minimize their carbon footprint and contribute to the circular economy.
Understanding the working principle of a plastic pipe extrusion line is crucial for manufacturers aiming to enhance production efficiency and product quality. Key components such as the extruder, die head, cooling system, and cutting mechanisms are essential for producing high-quality pipes. Technological advancements in automation, energy efficiency, and sustainability are optimizing the process, contributing to a more eco-friendly future in plastic pipe production. Companies like Jwell are leading the way with innovative solutions that improve production efficiency and product quality.
A: The plastic pipe extrusion line uses heat and pressure to melt raw plastic and form it into a continuous pipe. The extruder, die head, cooling system, and cutting mechanisms work together to produce high-quality pipes.
A: Common materials include PVC, PE, and PPR. These materials are melted and shaped by the extrusion line to create pipes for various applications.
A: The extrusion line ensures consistent temperature, pressure, and uniform material flow, producing pipes with precise dimensions and high strength.
A: Multi-layer extrusion lines provide enhanced pipe strength, insulation, and functionality, making them ideal for specific applications like oxygen barrier pipes.
A: Automation in extrusion lines improves efficiency by controlling temperature, pressure, and material flow, reducing errors and enhancing production speed.
A: Regular maintenance ensures smooth operation, prevents downtime, and maintains consistent quality by addressing issues like overheating or wear and tear.