- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search












Have you ever wondered how materials can combine the flexibility of rubber and the processability of plastic? This unique characteristic belongs to Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs).
In this article, we will explore what TPE material is, how it works, and its various applications. You’ll learn how TPE materials offer a perfect balance of performance, flexibility, and recyclability for a wide range of industries.
TPEs are a blend of polymers that exhibit the properties of both plastics and elastomers. They are made up of two key components: hard segments and soft segments. The hard segments provide the material with structural integrity and resistance to deformation, while the soft segments provide elasticity and flexibility. The unique structure of TPE allows it to be processed using conventional thermoplastic techniques such as injection molding, while still maintaining the rubber-like characteristics typically associated with elastomers.
These materials are often referred to as "rubber-like plastics" because they combine the best properties of both materials. TPEs do not require curing, unlike traditional rubber, and can be easily reprocessed and reshaped multiple times. This makes them highly suitable for mass production and recycling.
The dual-phase structure of TPE is what gives it its unique properties. The hard segments are typically crystalline or glassy thermoplastic polymers, while the soft segments are often amorphous and rubbery. When TPE is heated above its melting point, the hard segments become soft, allowing the material to be molded and shaped. Once cooled, the hard segments re-solidify, while the soft segments retain their elastic properties.
This behavior allows TPEs to be processed similarly to thermoplastics but to behave like elastomers under stress. The material can stretch, bend, and recover its original shape, making it highly durable and versatile.
TPEs differ from traditional elastomers and plastics in several ways. Unlike thermoset rubbers, which are chemically crosslinked and cannot be remolded, TPEs are recyclable and can be reheated and reprocessed without losing their physical properties. In comparison to traditional plastics, TPEs offer superior flexibility and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications that require both durability and elasticity.
TPEs also outperform some elastomers in certain applications because they can be processed using injection molding or extrusion, which allows for more complex shapes and designs. Additionally, TPEs can be blended with other materials, such as fillers or pigments, to enhance specific properties like hardness, color, or chemical resistance.
One of the most notable properties of TPE is its flexibility. TPE materials can be stretched and deformed, but they always return to their original shape once the force is removed. This ability to recover from deformation is due to the rubber-like nature of the soft segments in TPEs. Whether used in automotive seals, medical tubing, or consumer goods, the elasticity of TPE ensures long-lasting performance and durability.
TPEs are processed using conventional thermoplastic techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. These methods are cost-effective and efficient, allowing for high-volume production with minimal waste. Unlike traditional rubber, which requires curing and specialized equipment, TPEs can be processed using standard plastic manufacturing machinery. This makes TPEs a popular choice for manufacturers looking to optimize production costs and time.
Additionally, TPEs can be easily blended with other materials to modify their properties. For example, adding fillers or plasticizers can change the hardness or improve the material's resistance to wear and tear, providing more customization options.
TPEs are highly recyclable, which makes them an eco-friendly option for manufacturers looking to reduce waste. Since TPEs do not require curing or cross-linking, they can be reprocessed without compromising their physical properties. This ability to recycle and reuse TPE materials contributes to more sustainable manufacturing processes.
In addition to being recyclable, TPEs can also be made from bio-based or post-consumer materials, further enhancing their environmental benefits. Many manufacturers are now producing TPEs with a focus on sustainability, ensuring that the materials meet both performance and eco-friendly standards.
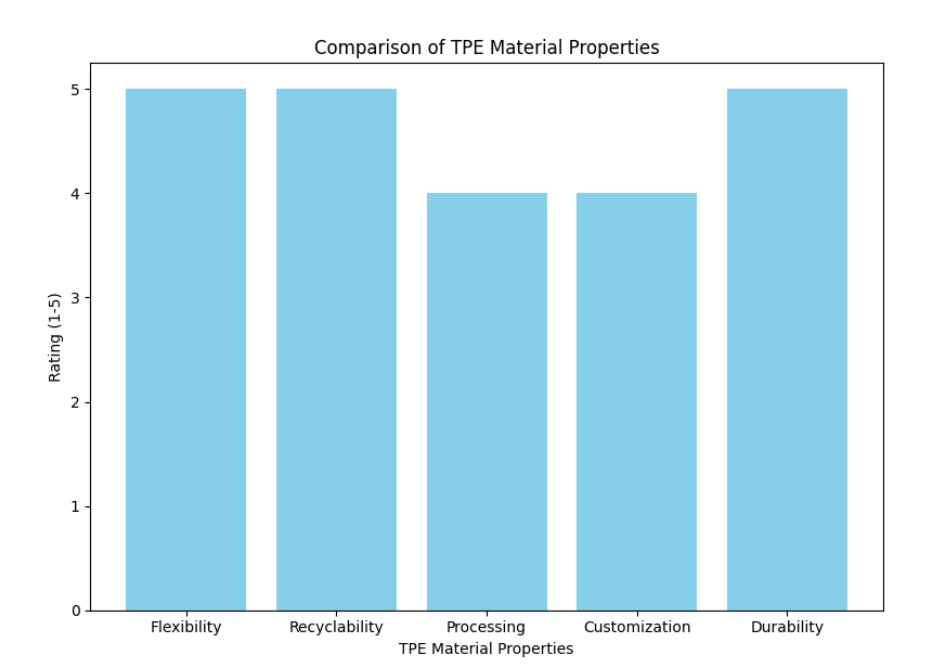
Property | TPE Material |
Flexibility | High |
Recyclability | Fully recyclable |
Processing | Easy (Injection, Molding) |
Customization | Customizable (Hardness, Color) |
Durability | Excellent |
TPEs come in various types, each designed to meet specific performance requirements. The most common types of TPEs include:
Styrenic block copolymers (SBC) are one of the most widely used types of TPEs. They are made by combining a hard polystyrene block with a soft elastomeric block, such as butadiene or isoprene. SBCs offer excellent processability and are often used in applications such as seals, gaskets, and footwear components. They are known for their flexibility, ease of processing, and low cost.
Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) are known for their excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and flexibility. TPUs are commonly used in applications requiring durability, such as automotive parts, medical devices, and industrial products. They offer superior performance in harsh environments and can withstand exposure to oils, chemicals, and UV light.
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV) are a type of TPE that is created by dynamically vulcanizing a rubber phase within a thermoplastic matrix. This results in a material with the durability and heat resistance of thermoset rubbers, but the processability of thermoplastics. TPVs are used in demanding applications such as automotive seals, gaskets, and hoses, where high-temperature and chemical resistance are required.
TPE Type | Applications |
SBC (Styrenic Block Copolymers) | Seals, Gaskets, Footwear |
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethanes) | Automotive Parts, Medical Devices |
TPV (Thermoplastic Vulcanizates) | High-Temperature Applications |
TPE-O (Polyolefin Elastomers) | Automotive, Industrial |
TPE-E (Copolyesters) | Electronics, Medical Devices |
Other types of TPEs include:
● TPE-O (Thermoplastic Olefins): Known for their low cost and good chemical resistance, TPE-O is commonly used in automotive and industrial applications.
● TPE-E (Thermoplastic Copolyesters): Offers high strength and heat resistance, making it suitable for applications in electronics and medical devices.
● TPE-A (Thermoplastic Polyamides): Provides excellent chemical and abrasion resistance, commonly used in industrial applications.
TPEs are extensively used in the automotive industry for various components, including seals, vibration dampeners, and soft-touch surfaces. TPEs provide excellent durability and resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals found in automotive environments. They also offer flexibility and ease of processing, which makes them ideal for use in high-volume automotive manufacturing.
Medical-grade TPEs are biocompatible, making them suitable for use in medical devices such as tubing, seals, and grips. These materials are resistant to sterilization processes like autoclaving and gamma irradiation, ensuring that they remain safe and effective for long-term use. The ability to customize TPEs for softness and flexibility also makes them ideal for medical applications that require comfort and durability.
TPEs are commonly found in everyday consumer goods such as toothbrush handles, toys, phone cases, and kitchen utensils. Their flexibility, durability, and ease of processing make them ideal for creating products that require both comfort and performance. In the electronics industry, TPEs are used for wire insulation and connectors, providing moisture resistance and flexibility in low-voltage applications.
TPEs are used in a variety of industrial applications, including tool handles, gaskets, and vibration damping. Their ability to withstand repeated mechanical stress and environmental exposure makes them ideal for products used in manufacturing and heavy-duty industries.
TPEs offer several advantages over other materials, including:
● Easy Processing: TPEs can be processed using standard thermoplastic techniques, which reduces manufacturing time and costs.
● Recyclability: TPEs are recyclable, making them an eco-friendly option for manufacturers.
● Flexibility and Durability: TPEs maintain their elasticity and strength, even under repeated stress and exposure to harsh conditions.
● Design Flexibility: TPEs can be easily molded into complex shapes and customized for hardness, color, and texture.
Despite their many benefits, TPEs do have some limitations:
● Performance at High Temperatures: TPEs lose stability at elevated temperatures, which can limit their use in high-heat applications.
● Chemical Resistance: While TPEs offer good resistance to many chemicals, they may not perform well in harsh chemical environments.
● Cost: TPEs can be more expensive than traditional rubbers or plastics, which may not make them the most cost-effective option for some applications.
When selecting a TPE for a specific application, consider factors such as:
● Hardness: Choose a TPE with the appropriate hardness for your application. TPEs can range from soft, flexible materials to rigid, tough materials.
● Temperature Resistance: If your application involves exposure to high temperatures, ensure that the TPE you select has the necessary heat resistance.
● Flexibility: Consider how much flexibility is needed for your application. TPEs can be formulated to offer varying degrees of flexibility.
TPEs offer a versatile and sustainable solution by combining the best features of thermoplastics and elastomers. Their ease of processing, recyclability, and customization make them ideal for applications across industries like automotive and healthcare.
By understanding the properties and types of TPEs, manufacturers can select the right material for their needs. When choosing a TPE solution, always consider the specific environmental and performance requirements to ensure optimal results. For tailored TPE solutions, Jwell offers reliable and high-performance options to meet diverse application needs.
A: TPE material stands for Thermoplastic Elastomers, a class of polymers that combine the properties of elastomers (rubber-like flexibility) and thermoplastics (easy processing). It offers the best of both worlds: flexibility and the ability to be molded and remolded.
A: TPE material is highly customizable, offering benefits like recyclability, easy processing, and flexibility. It’s widely used in automotive, medical, and consumer products due to its durability and performance.
A: TPE material is processed using standard thermoplastic techniques, such as injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. This makes it easy to form complex shapes and reuse the material multiple times.
A: TPE material is used in many industries, including automotive, medical devices, electronics, and consumer goods. Its flexibility, recyclability, and durability make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
A: Yes, TPE material is fully recyclable. It can be reprocessed without losing its properties, making it an eco-friendly choice compared to other materials.