- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search












Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB) is an essential material in modern manufacturing. It plays a crucial role in laminated glass, providing safety and durability. In this article, we will explore PVB's key features and its importance in various industries. You'll learn how PVB enhances safety, design, and functionality in products like automotive windshields and architectural glass.
Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB) is a thermoplastic resin created by reacting polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with butyraldehyde. This reaction results in a clear, flexible, and adhesive material. PVB is primarily produced as a thin film and is commonly used as an interlayer in laminated glass.
The manufacturing process of PVB involves several stages: extrusion, lamination, and film production. During extrusion, PVB resin is heated and pressed through molds to form films of various thicknesses. This PVB film is then sandwiched between glass layers and subjected to high heat and pressure in an autoclave to create laminated glass. This process bonds the PVB film to the glass, creating a composite that offers improved safety, sound insulation, and UV protection.
PVB is known for its impressive properties, including:
● Transparency: PVB maintains a high level of clarity, which is crucial for both aesthetic and functional purposes in applications like automotive windshields and architectural glass.
● Flexibility and Strong Adhesion: PVB adheres strongly to glass, creating a durable bond that enhances the structural integrity of laminated glass.
● Impact Resistance and UV Protection: PVB provides excellent protection against impacts, reducing the risk of glass shattering. It also blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays, which helps protect interiors from fading.
The primary function of PVB in laminated glass is to enhance safety. PVB acts as a shock absorber, preventing glass from shattering into sharp, dangerous fragments during an impact. This property is especially important in automotive applications, where windshields are required to maintain structural integrity during accidents.
In architectural applications, PVB ensures that glass remains intact after impact, preventing injury and damage. This is why laminated glass with a PVB interlayer is commonly used in high-traffic areas, residential windows, and commercial buildings.
Another significant benefit of PVB is its ability to block ultraviolet (UV) radiation. By filtering out up to 99% of UV rays, PVB helps prevent the fading of furniture, carpets, and other interior elements. This makes it an ideal choice for windows in buildings exposed to direct sunlight.
Additionally, PVB acts as an effective sound insulator. It absorbs sound waves and reduces noise transmission, making laminated glass with PVB an excellent choice for applications where noise reduction is important, such as in urban buildings or vehicles.
Benefit | Description |
Safety | Prevents glass from shattering into sharp fragments, reducing injury risk. |
UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays, protecting interiors from fading. |
Sound Insulation | Reduces noise transmission, creating a quieter environment. |
Impact Resistance | Enhances the durability of glass, preventing breakage under force. |
Design Flexibility | Available in various colors, thicknesses, and finishes for diverse applications. |
PVB has been a crucial component in automotive safety for decades. In windshields, PVB interlayers prevent glass from shattering upon impact, keeping passengers safe during collisions. The flexibility and durability of PVB make it an essential part of car windshields, which are subjected to significant force during crashes.
In addition to its safety benefits, PVB’s noise reduction properties also make it beneficial in automotive applications, providing a quieter ride for passengers.
In architectural applications, PVB is used in a variety of glass products, including windows, skylights, and facades. The durability, impact resistance, and UV-blocking properties of PVB make it an excellent choice for both safety and aesthetics.
Architects often select laminated glass with PVB for its ability to improve energy efficiency, as it provides insulation and helps maintain indoor temperatures. It also contributes to the aesthetic value of buildings, as PVB can be customized in different colors and thicknesses to match design requirements.
Beyond its use in automotive and architectural applications, PVB is also utilized in the solar industry as a backsheet material for solar panels. PVB’s impact resistance and optical clarity make it an ideal material for encapsulating solar cells and ensuring their durability.
PVB is also used in decorative glass products, including furniture, railings, and staircases, where its flexibility, transparency, and ease of customization are highly valued.
One of the primary reasons PVB is used in laminated glass is its ability to enhance safety. In the event of an impact, the PVB interlayer holds the glass together, preventing shards from flying and reducing the risk of injury. This is particularly crucial in applications such as automotive windshields, where safety is paramount.
In addition to its impact resistance, PVB offers protection against forced entry. Laminated glass with PVB interlayers is often used in security applications, such as bulletproof windows and glass doors, where additional protection is required.
Laminated glass with PVB interlayers provides excellent sound insulation, making it ideal for noise-sensitive environments. This is particularly beneficial in urban buildings near busy streets, as well as in vehicles, where a quieter ride improves comfort.
PVB also contributes to energy efficiency. The interlayer helps to reduce heat transfer, making laminated glass more effective at maintaining indoor temperatures. This can lead to lower heating and cooling costs, making it a sustainable option for energy-conscious building designs.
PVB is available in a variety of colors, thicknesses, and finishes, allowing for a high degree of design flexibility. Whether used in automotive, architectural, or decorative applications, PVB can be tailored to meet specific aesthetic requirements. The ability to create customized laminated glass enhances the versatility of PVB, making it a preferred choice for designers and architects alike.
The thickness of the PVB interlayer can significantly affect the performance of laminated glass. Thicker PVB films provide better impact resistance, sound insulation, and UV protection, making them ideal for applications that require higher safety standards, such as automotive windshields and high-security buildings.
For automotive applications, the standard PVB thickness typically ranges from 0.38 mm to 0.76 mm. In architectural applications, thicker films may be used to enhance soundproofing and energy efficiency.
While thicker PVB films offer several benefits, they may also introduce trade-offs. For example, thicker films can reduce the optical clarity of the glass, making it slightly less transparent. Additionally, the increased weight and cost of thicker PVB films may not always be necessary for certain applications, such as decorative glass.
When selecting the appropriate thickness, it is essential to balance performance enhancements with the practical considerations of cost and design requirements.
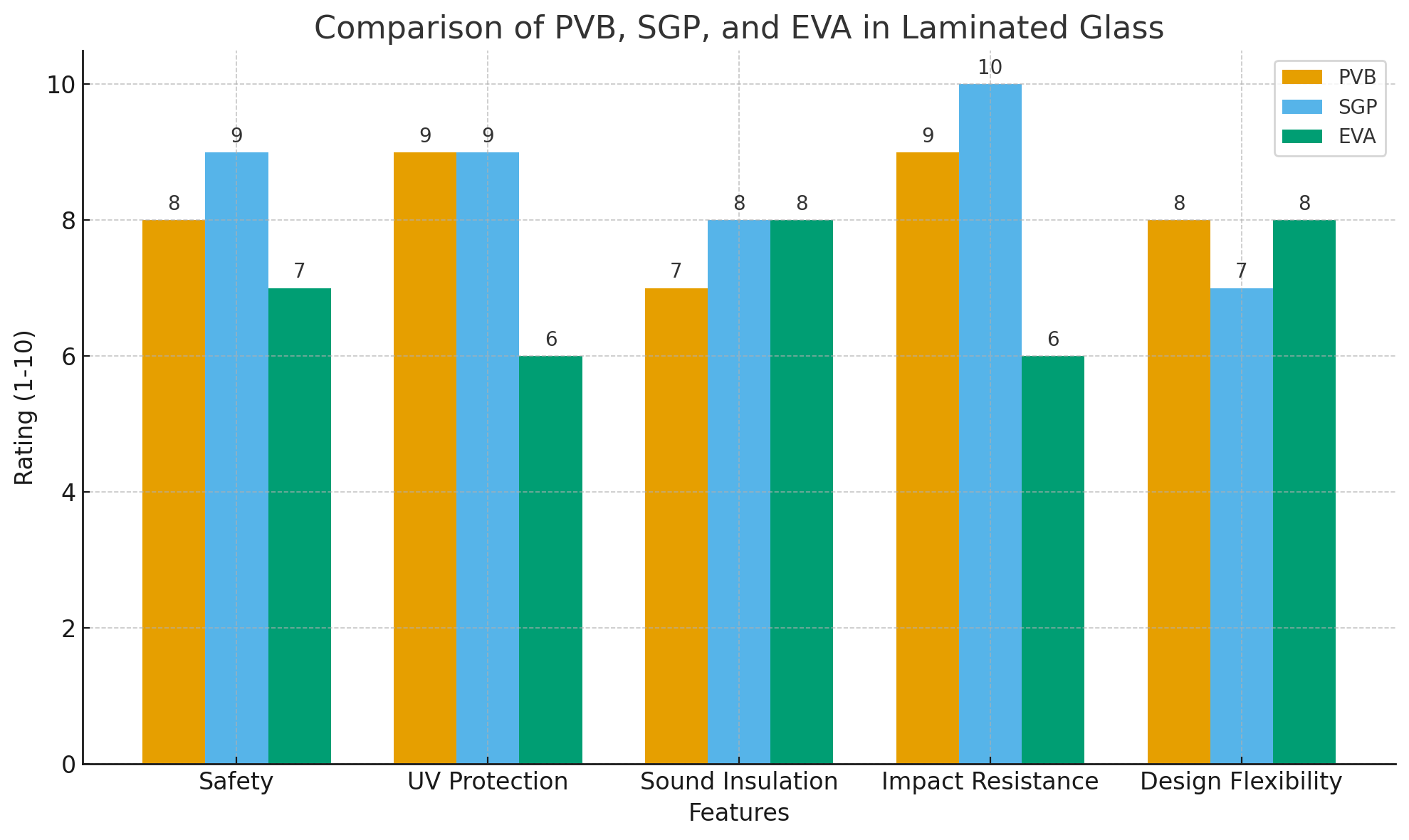
SentryGlas Plus (SGP) is an alternative to PVB that offers superior strength and rigidity. Compared to PVB, SGP is 100 times more rigid and five times more resistant to tearing, making it ideal for high-security applications, such as bulletproof glass and glass used in extreme conditions.
However, SGP is generally more expensive than PVB and is not as widely used due to its higher cost. It is typically selected for applications where superior strength is required, such as frameless glass balustrades and canopies.
EVA is another alternative to PVB, particularly valued for its moisture resistance. While it does not offer the same level of impact resistance as PVB or SGP, it is often used in applications where UV protection and transparency are prioritized. EVA is commonly used in decorative laminated glass and some solar panels.
While EVA offers advantages in moisture resistance, it is not as durable as PVB in terms of impact resistance, making it less suitable for applications that require high levels of safety.
Benefit | Description |
Safety | Prevents glass from shattering into sharp fragments, reducing injury risk. |
UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays, protecting interiors from fading. |
Sound Insulation | Reduces noise transmission, creating a quieter environment. |
Impact Resistance | Enhances the durability of glass, preventing breakage under force. |
Design Flexibility | Available in various colors, thicknesses, and finishes for diverse applications. |
Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB) is a key material in laminated glass production, offering safety, UV protection, sound insulation, and design flexibility. Its strong adhesion and impact resistance make it the preferred choice for automotive, architectural, and solar panel applications. As demand for safer, energy-efficient glass products rises, PVB continues to lead in innovation. For tailored solutions, Jwell offers reliable products that meet diverse industry needs with unmatched quality and performance.
A: PVB, or Polyvinyl Butyral, is primarily used as an interlayer in laminated glass. It enhances safety, provides UV protection, and offers sound insulation in automotive, architectural, and solar panel applications.
A: PVB is essential in laminated glass due to its strong adhesion to glass, impact resistance, and ability to hold shattered glass together, making it safer and more durable.
A: PVB improves safety by preventing glass from shattering into sharp pieces. It keeps the glass layers intact, reducing the risk of injury during accidents.
A: PVB offers several benefits in windows, including UV protection, noise reduction, and enhanced safety, making it ideal for both automotive and architectural glass.
A: While PVB is more cost-effective than alternatives like SGP, its price varies based on thickness and application. It provides a balanced option for safety and performance.
A: PVB's insulation properties help reduce heat transfer, improving energy efficiency in buildings and vehicles, and lowering heating and cooling costs.