- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search



Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-17 Origin: Site









Have you ever wondered what tiny plastic pellets can become? These small granules are the foundation of countless products. Plastic pelletizing machines play a crucial role in transforming raw materials into these versatile pellets. In this post, you'll learn what plastic pellets are, the importance of pelletizing machines, and an overview of the pelletizing process.
Plastic pellets serve as the building blocks for countless products across various industries. Their versatility and adaptability make them essential in modern manufacturing. Let's explore some key applications where plastic pellets play a vital role.
Plastic pellets are widely used to create packaging materials. They form containers, bottles, wraps, and films that protect food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and more. These pellets offer several advantages in packaging:
Durability: They shield contents from moisture, contamination, and damage.
Printability: Packaging made from pellets can be easily printed, labeled, or hot-stamped, enhancing brand visibility.
Lightweight: Products remain easy to transport and handle.
Barrier Properties: They help preserve freshness and extend shelf life.
For example, polyethylene (PE) pellets are common in flexible food wraps, while polypropylene (PP) pellets often make sturdy containers and caps.
Plastic pellets are key in manufacturing parts for electronics and appliances. They create casings, buttons, and internal components that need to be durable yet lightweight. Using different pellet types and colors allows designers to create stylish, functional products.
Typical uses include:
TV and remote control housings
Computer keyboards and mice
Refrigerator and washing machine panels
The flexibility of plastic pellets enables intricate designs and textures, improving both aesthetics and user experience.
The automotive industry relies heavily on plastic pellets for interior and exterior parts. They help reduce vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency and lowering emissions. Common components made from pellets include:
Dashboards and door panels
Seat components and buckles
Wheel covers and trim pieces
Plastic parts also offer design versatility, allowing car makers to customize colors and finishes to appeal to various consumer preferences.
Plastic pellets contribute to building materials that offer durability and ease of installation. Examples include:
Insulation mats and foams
Pipe fittings and profiles
Decorative ceiling and wall panels
Compared to traditional materials, plastic-based components provide better toughness and resistance to weathering. Their color and texture can be tailored to fit architectural needs.
Plastic pellets come in many types, each with unique properties making them suitable for different uses. Knowing these types helps manufacturers pick the right pellet for their products. Let’s explore some common plastic pellets and their characteristics.
Polyethylene is one of the most widely used plastics. It comes mainly in two forms:
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Strong and rigid. Used for making bottles, pipes, and containers. It resists chemicals and moisture well.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE): More flexible and softer. Common in plastic bags, wraps, and squeeze bottles.
PE pellets are durable, moisture-resistant, and easy to process. These qualities make them popular in packaging and consumer goods.
Polypropylene pellets are lightweight and heat-resistant. They handle high temperatures better than many plastics, which suits them for dishwasher-safe containers and automotive parts.
PP is tough and flexible, often used in:
Food containers
Medical syringes
Automotive trim parts
Its resistance to fatigue and chemicals makes it ideal for reusable products.
PVC pellets produce a strong, weather-resistant plastic. This plastic is versatile and used in construction (pipes, window frames), medical tubing, and electrical cable insulation.
PVC can be rigid or flexible depending on additives. It withstands chemicals and sunlight well but has some recycling challenges due to these additives.
Growing environmental concerns have led to biodegradable and recycled pellets gaining popularity.
Biodegradable Pellets: Made from materials like polylactic acid (PLA). They break down naturally over time. Used in compostable packaging, disposable cutlery, and some medical products.
Recycled Pellets: Made by processing post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste. They reduce reliance on virgin plastics and help cut down waste.
These sustainable pellets often match the performance of traditional plastics but have a lower environmental footprint.
| Pellet Type | Key Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Durable, moisture-resistant | Bottles, bags, containers |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Lightweight, heat-resistant | Food containers, auto parts |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Strong, weather-resistant | Pipes, medical tubing, cables |
| Biodegradable Pellets | Compostable, eco-friendly | Compostable packaging, cutlery |
| Recycled Pellets | Sustainable, cost-effective | Packaging, textiles, construction |
Choosing the right plastic pellet depends on the product’s needs for strength, flexibility, heat resistance, and environmental impact. As demand for greener products rises, biodegradable and recycled pellets are becoming more common alongside traditional types.
This variety ensures plastic pellets remain versatile, supporting industries from packaging to automotive while moving toward sustainable practices.
Plastic pellets, though small, pose big environmental challenges. These tiny granules often escape during manufacturing, transportation, or handling. Once in the environment, they become a major source of microplastic pollution, especially in oceans.
Marine Life Threats: Sea creatures mistake pellets for food. Ingesting them causes physical harm, blockages, or even death.
Toxin Carriers: Pellets absorb harmful chemicals from water. These toxins enter the food chain, affecting animals and humans.
Ecosystem Damage: Pellets disrupt habitats like coral reefs and seabeds, harming biodiversity.
Economic Costs: Plastic pollution causes billions in damage to fisheries, tourism, and marine ecosystems annually (example data, needs verification).
The problem is vast — estimates suggest around 10 trillion pellets enter waterways yearly. Without action, pollution will worsen, threatening ocean health and human well-being.
Recycling plastic pellets offers a way to reduce waste and environmental harm. Here’s how it works:
Collection: Post-consumer or industrial plastic waste is gathered.
Cleaning: Contaminants are removed to ensure pellet quality.
Processing: Waste is melted and reformed into new pellets.
Reuse: Recycled pellets replace virgin materials in manufacturing.
Using recycled pellets lowers demand for new plastic, conserves resources, and cuts pollution. For example, recycled polyethylene pellets can be remade into containers, packaging, or fibers.
However, challenges remain:
Quality Control: Recycled pellets must meet strict standards to perform well.
Additive Residues: Some plastics contain additives that complicate recycling.
Market Demand: Manufacturers need incentives to use recycled materials.
Despite these hurdles, recycled pellets are gaining popularity as industries pursue sustainability.
Many companies and organizations now lead efforts to reduce pellet pollution and promote sustainability:
Operation Clean Sweep: An industry program teaching best practices to prevent pellet spills during production and transport.
Corporate Accountability: Groups like As You Sow push manufacturers to improve pellet handling and transparency.
Advanced Technologies: Innovations in pelletizing machines reduce waste and improve efficiency.
Regulatory Pressure: Some regions enact laws requiring better plastic waste management.
Manufacturers also design equipment with spill prevention features and provide training on safe pellet handling.
Together, these initiatives aim to:
Minimize pellet loss to the environment.
Encourage recycling and reuse.
Raise awareness about pellet pollution.
Foster collaboration across the supply chain.
Sustainability in plastic pellet production and use is crucial. It balances the benefits of plastic products with protecting ecosystems and public health.
Plastic pellets are more than just raw materials for industrial products. Their unique properties make them perfect for creative and therapeutic uses too. Let’s dive into some surprising ways plastic pellets add value beyond traditional manufacturing.
Plastic pellets bring versatility and texture to many craft projects. Artists and hobbyists use them to add weight, bulk, or interesting surfaces to their creations. Here are some popular craft uses:
Mosaic Art: Pellets add a 3D texture to mosaics, creating eye-catching designs.
Jewelry Making: Mixed with resin, pellets produce lightweight, colorful beads and pendants.
Model Scenery: They simulate gravel, sand, or soil in model train sets and dioramas.
Rock Tumbling Media: Pellets cushion stones during polishing, preventing chips and cracks.
These applications highlight pellets’ durability and ease of use. They’re easy to handle, clean, and mold into artistic forms. Many crafters also choose recycled pellets to support eco-friendly practices.
Plastic pellets play a special role in therapy and sensory development. Their smooth, uniform texture makes them ideal for calming, tactile activities. Common uses include:
Sensory Bags: Filled with pellets and small objects, these bags help children improve fine motor skills and focus.
Therapeutic Toys: Pellets provide a soothing tactile experience, often used in tools for children with sensory processing disorders.
Weighted Blankets: Pellets add gentle, evenly distributed weight, helping reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality.
For example, many weighted blankets use plastic pellets to balance comfort and flexibility. Pellets are non-toxic, washable, and maintain consistent weight, making them safe for therapeutic use.
Plastic pellets add realistic weight and flexibility to dolls, enhancing their lifelike feel. They help dolls maintain posture and provide a comforting heft. This is especially useful for collectible dolls or therapeutic toys.
In weighted blankets, pellets ensure even pressure across the fabric. This pressure mimics a calming hug, which can soothe stress and promote relaxation. Brands often select pellets for their consistent size, non-toxicity, and ease of care.
Safety Note: Pellets used in toys and blankets must be securely enclosed to prevent choking hazards. Choosing high-quality, non-toxic pellets is essential.
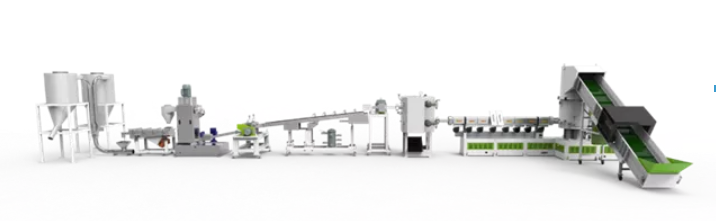
Plastic pelletizing machines transform raw plastic materials into small, uniform pellets. These pellets become the building blocks for countless plastic products. Understanding how these machines work helps us appreciate the manufacturing process and the technology behind plastic production.
Feeding Raw MaterialThe process begins by feeding plastic raw materials—either virgin resin or recycled plastic—into the machine’s hopper. These materials may come as flakes, powders, or chunks.
Melting and MixingInside the extruder, the plastic is heated until it melts. A screw pushes the molten plastic forward while mixing it thoroughly. This step ensures uniform consistency and blends any additives or colorants.
Extrusion Through a DieThe melted plastic is forced through a die, shaping it into continuous strands. The die determines the pellet size and shape, usually cylindrical or spherical.
Cooling the StrandsThe hot strands exit the die and enter a cooling system, often a water bath or air cooling chamber. Cooling solidifies the plastic, preserving its shape and making it easier to handle.
Cutting into PelletsA rotating blade or pelletizer cuts the cooled strands into small, uniform pellets. The pellet size can be adjusted by changing the blade speed or die dimensions.
Drying and ScreeningPellets may contain moisture after cooling. Dryers remove excess water to prevent clumping. Then, screening equipment filters out oversized or undersized pellets, ensuring quality and uniformity.
PackagingFinally, the pellets are collected and packaged for shipment to manufacturers who use them to make plastic products.
Modern pelletizing machines incorporate advanced features to improve efficiency and product quality:
Automated Controls: Sensors and computer systems monitor temperatures, pressures, and speeds, optimizing the process and reducing waste.
Energy Efficiency: Newer machines consume less power by improving heating zones and screw design.
Enhanced Cooling Systems: Improved water or air cooling methods speed up production while maintaining pellet quality.
Modular Design: Machines can be customized with different dies or pelletizers to handle various plastic types and pellet sizes.
Waste Reduction: Some systems recycle scrap material generated during pelletizing, feeding it back into the process.
Proper maintenance keeps pelletizing machines running smoothly and extends their lifespan:
Regular Cleaning: Residue buildup can cause contamination and affect pellet quality. Cleaning screw barrels, dies, and cutters prevents this.
Lubrication: Moving parts need regular lubrication to avoid wear and tear.
Blade Sharpening: Cutting blades must stay sharp for uniform pellet size and to prevent machine strain.
Monitor Temperatures: Overheating can degrade plastic; maintaining correct temperature profiles is critical.
Check for Wear: Screws, barrels, and dies wear over time; timely replacement avoids downtime.
Calibrate Sensors: Accurate sensors ensure process parameters remain within set limits.
Following these tips improves machine uptime, reduces defects, and lowers operational costs.
Plastic pellets are essential in packaging, electronics, automotive, and construction industries due to their versatility. Future trends in plastic pelletizing include advancements in recycling and eco-friendly materials. Companies like Changzhou Dyun Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. are leading the way with innovative solutions, offering products that enhance sustainability and efficiency. By adopting sustainable practices, industries can reduce environmental impact while maintaining product quality, highlighting the importance of responsible plastic pellet use.
A: Plastic pellets are used in packaging, electronics, automotive, construction, crafts, therapy, and more.
A: Common types include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), biodegradable, and recycled pellets.
A: They melt, mix, extrude, cool, cut, dry, and package raw plastic materials into uniform pellets.
A: They contribute to microplastic pollution, affecting marine life and ecosystems.
A: Through recycling, industry initiatives, and sustainable practices.